

Next: Detectors
Up: INSTRUMENTATION
Previous: Operational items
It is also possible to use interference effects to measure spectral energy
distributions instead of a dispersing element. The Fabry-Perot is an
example of such a type of instrument, although it does not record all
wavelengths simultaneously.
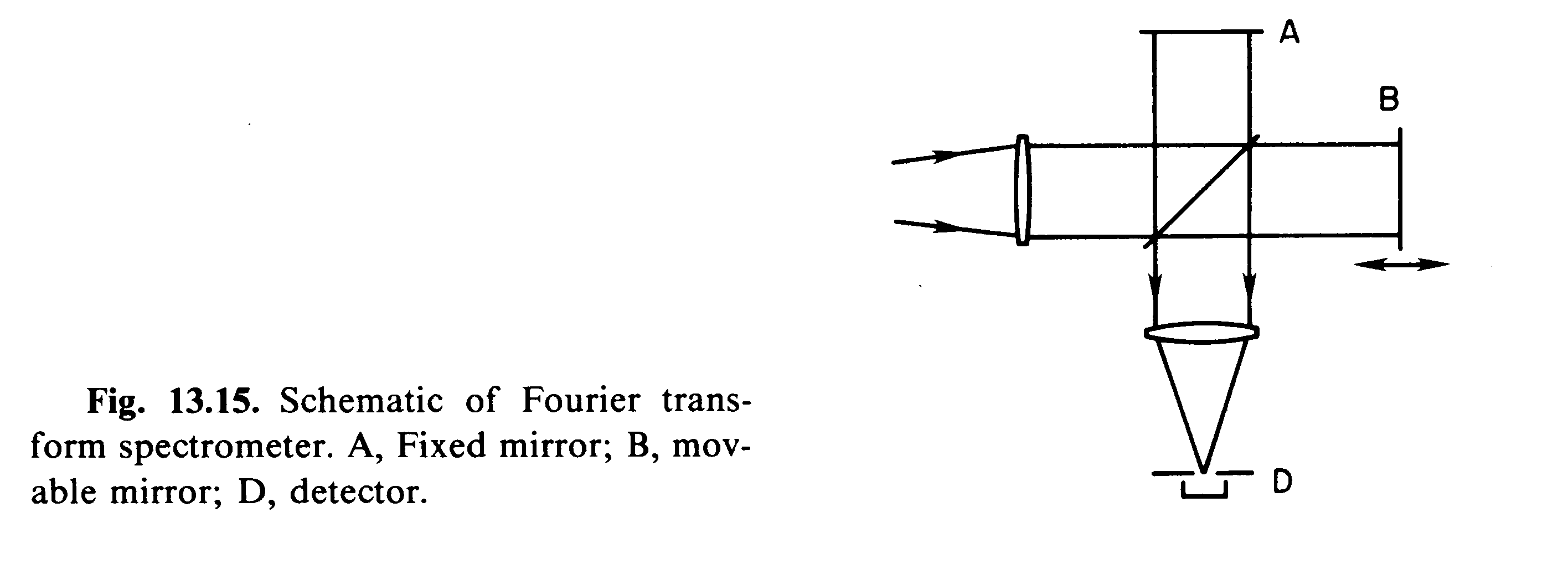 Another instrument which uses interference to infer spectroscopy information
is the Fourier Transform Spectrometer (FTS), which is basically a
scanning Michaelson interferometer. The light from the source is split
into two parts using a beamsplitter. One part of light is reflected off
a fixed flat mirror and the other is reflected off a mirror which can
be moved laterally. The two images are combined to form fringes. The
fringe pattern changes as the path length of the second beam is changed.
The intensity modulation for a given wavelength (
Another instrument which uses interference to infer spectroscopy information
is the Fourier Transform Spectrometer (FTS), which is basically a
scanning Michaelson interferometer. The light from the source is split
into two parts using a beamsplitter. One part of light is reflected off
a fixed flat mirror and the other is reflected off a mirror which can
be moved laterally. The two images are combined to form fringes. The
fringe pattern changes as the path length of the second beam is changed.
The intensity modulation for a given wavelength (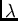 ) or
wavenumber (
) or
wavenumber (
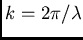 ) is given by:
) is given by:
and the flux after integrating over all wavelengths is:
where 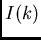 is the input spectrum. Consequently it is possible to recover
the input spectrum by taking the Fourier cosine transform of the
recorded intensity. In practice, a discrete Fourier transform is used.
is the input spectrum. Consequently it is possible to recover
the input spectrum by taking the Fourier cosine transform of the
recorded intensity. In practice, a discrete Fourier transform is used.
The FTS requires scanning in path spacing. But unlike the Fabry-Perot, it
yields information on intensity at all wavelengths simultaneously.


Next: Detectors
Up: INSTRUMENTATION
Previous: Operational items
Rene Walterbos
2003-04-14

